Python 簡易手冊
單元 28 - with 陳述
關鍵字 (keyword) with 用來將資料 (data) 轉換成內容管理員 (context manager) 物件 (object) ,典型的例子是處理檔案,例如有以下的文字檔案 demo.txt
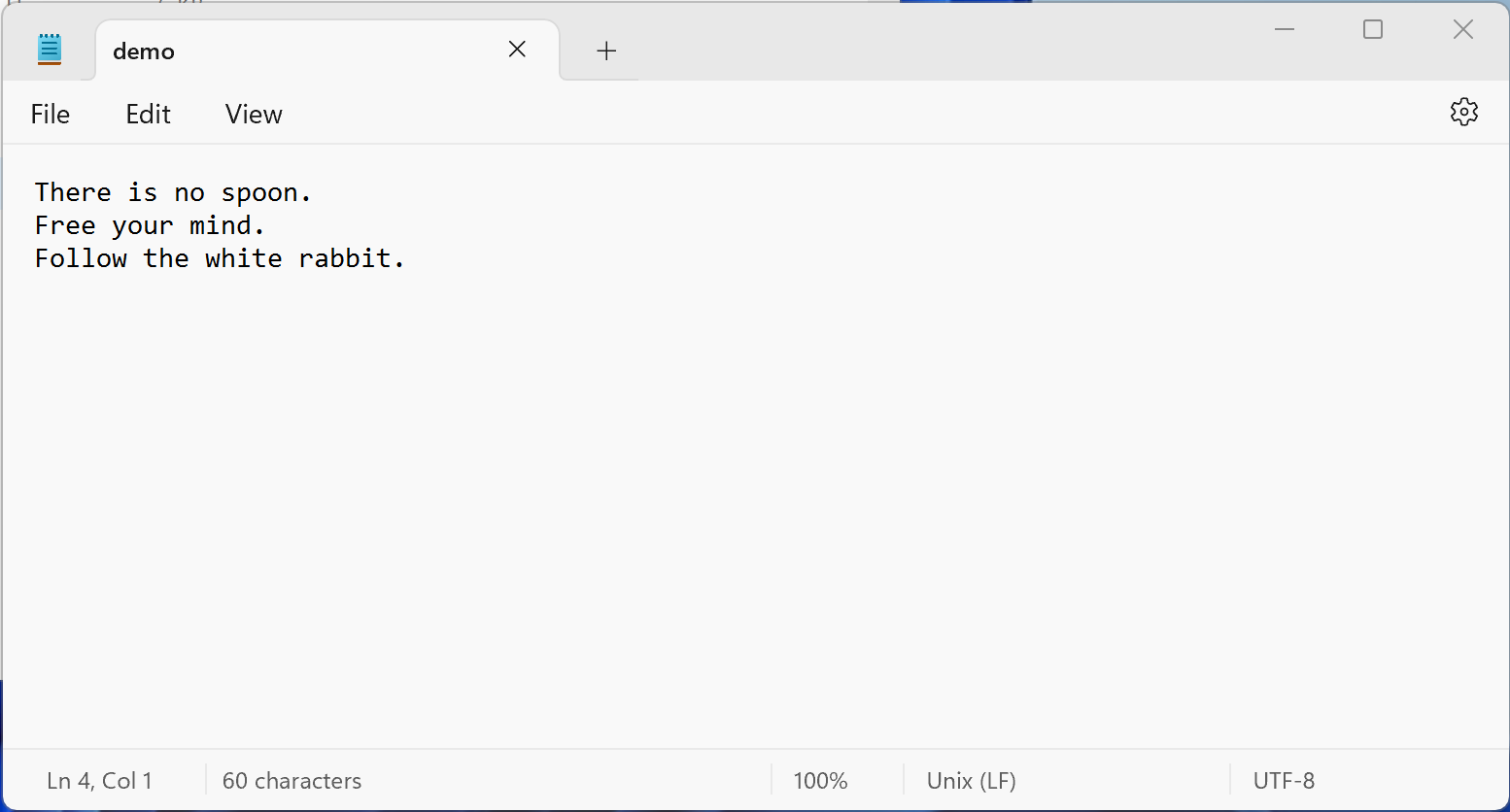
以下程式可以在命令列印出檔案內容
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | # 進行檔案讀取 with open('demo.txt', 'r') as f: # 依次印出檔案中的每一行 for s in f.readlines(): print(s, end="") print() # 檔名: with_demo.py # 說明: 《Python簡易手冊》的範例 # 網址: http://kaiching.org # 作者: Kaiching Chang # 時間: 2024 年 3 月 |
這裡是用內建函數 (built-in function) open() 開啟檔案,底下第一個引數 (argument) 為檔案名稱字串 (string) ,第二個引數則是模式 'r' , 'r' 表示讀取
1 2 | # 進行檔案讀取 with open('demo.txt', 'r') as f: |
單元 44 - 函數與 return 陳述會介紹如何定義函數 (function) 及函數的用法。
open() 後面需要加上關鍵字 as , as 後面接自訂的識別字 (identifier) f , f 就是 open() 回傳的檔案物件,在底下就是直接用 f 在命令列印出內容
3 4 5 | # 依次印出檔案中的每一行 for s in f.readlines(): print(s, end="") |
檔案物件的 readlines() 方法 (method) 取得文字檔案內容後,依換行符號分成字串元素 (element) ,這裡是用 for 迴圈一次取得每一行的內容並且印出,執行結果如下
| > python with_demo.py |
There is no spoon. Free your mind. Follow the white rabbit. |
| > |
單元 23 - for 陳述詳細介紹 for 的用法。
單元 55 - 實體屬性與方法會介紹如何定義物件的實體方法。
關鍵字 with 其實是 Python 後來加入的語法糖,因為本來用內容管理員物件,使用完畢都要手動關閉內容管理員物件,不然該物件會一直佔用記憶體, with 是讓內容管理員物件在 with 陳述 (statement) 之後自動關閉,所以除了可以減少程式碼行數外,也少了忘記關閉的問題。
如果一次要處理多個檔案, with 後面可以加上小括弧,小括弧內以逗點區隔每個 as 運算式 (expression) ,例如以下程式將 demo.txt 的內容寫入 demo2.txt 中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | # 打開一個檔案將內容寫入另一個檔案 with (open('demo.txt', 'r') as f1, open('demo2.txt', 'w') as f2, ): # 依次寫入檔案中的每一行 for s in f1.readlines(): f2.write(s) # 檔名: with_demo2.py # 說明: 《Python簡易手冊》的範例 # 網址: http://kaiching.org # 作者: Kaiching Chang # 時間: 2024 年 3 月 |
注意開啟 demo2.txt 的模式改成 'w' ,模式 'w' 就是寫入,另外在檔案不存在的情況下會建立新檔案
3 | open('demo2.txt', 'w') as f2, |
寫入檔案是用檔案物件的 write() 方法,這裡取得 f1 中的每一行後,依次呼叫 write() 寫入 f2 中
5 6 7 | # 依次寫入檔案中的每一行 for s in f1.readlines(): f2.write(s) |
執行這個程式會無聲無息跳到下一行
| > python with_demo2.py |
| > |
相同路徑下就多了 demo2.txt , demo.txt 的內容已經複製到 demo2.txt 中
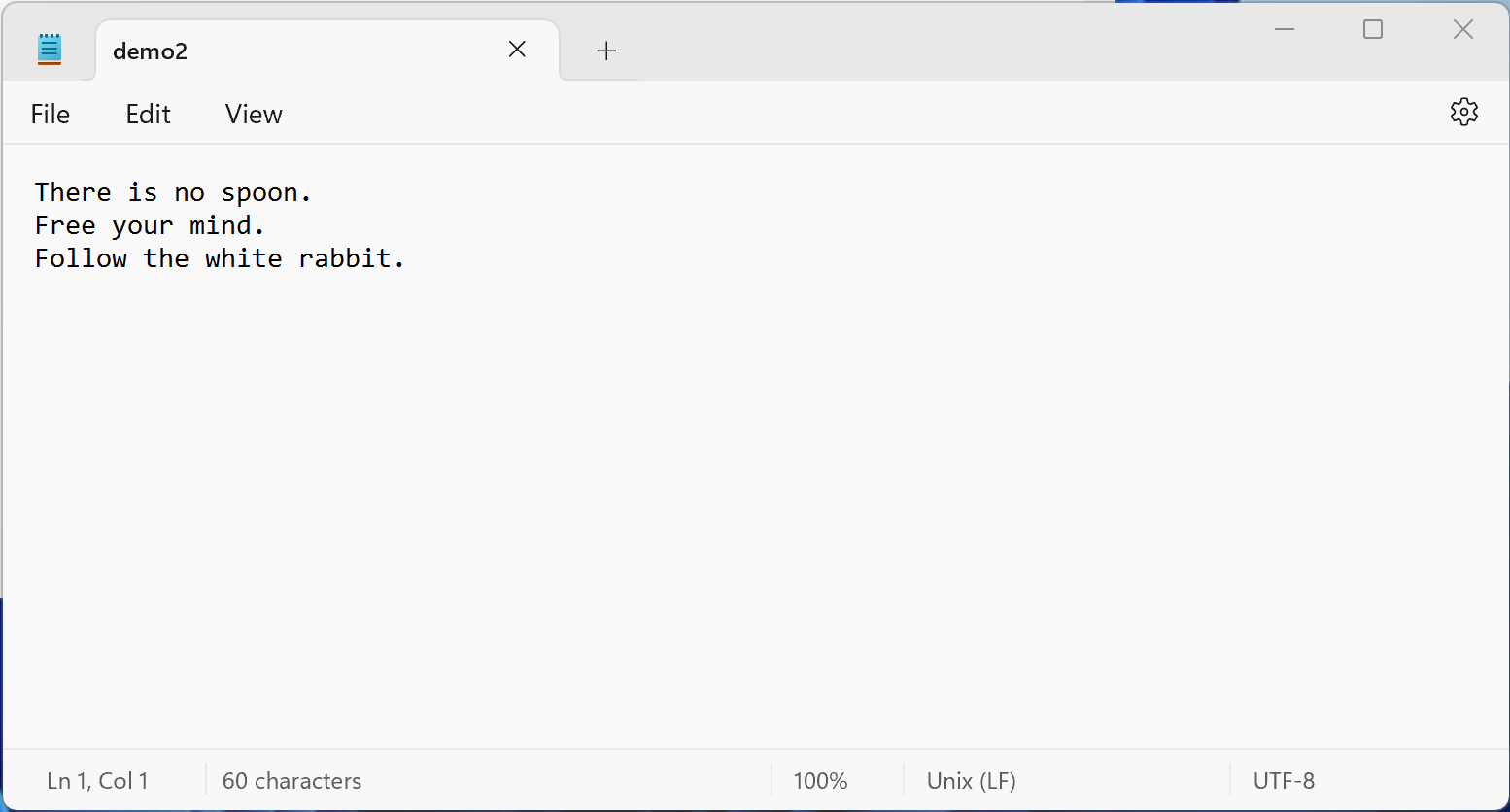
不過要注意,以上是處理 Unicode 編碼的文字檔案,如果不是處理 Unicode 編碼的檔案,模式要加上 'b' ,舉例如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | # 進行檔案讀取 with (open('demo2.txt', 'r') as f1, open('demo3.txt', 'rb') as f2, ): # 取得 f1 的內容 c1 = f1.read() # 印出 f1 內容的型態 print(type(c1)) # 取得 f2 的內容 c2 = f2.read() # 印出 f2 內容的型態 print(type(c2)) # 檔名: with_demo3.py # 說明: 《Python簡易手冊》的範例 # 網址: http://kaiching.org # 作者: Kaiching Chang # 時間: 2024 年 3 月 |
上面分別以 demo2.txt 與 demo3.txt 為例, demo2.txt 如上例產出,其為 Unicode 編碼,而 demo3.txt 則是 Big5 編碼,這裡先用 read() 讀取檔案內容,再印出檔案內容物件的資料型態,執行結果如下
| > python with_demo.py |
<class 'str'> <class 'bytes'> |
| > |
單元 36 - Unicode會介紹如何處理非 Unicode 編碼的問題。
簡單說,檔案如果是 Unicode 編碼,那取得的內容就是字串,反之如果不是 Unicode ,那取得的內容會是 bytes 型態。
單元 37 - 二進制序列會詳細介紹 bytes 型態。
參考資料
- https://docs.python.org/3/reference/compound_stmts.html#the-with-statement
- https://docs.python.org/3/tutorial/inputoutput.html#reading-and-writing-files